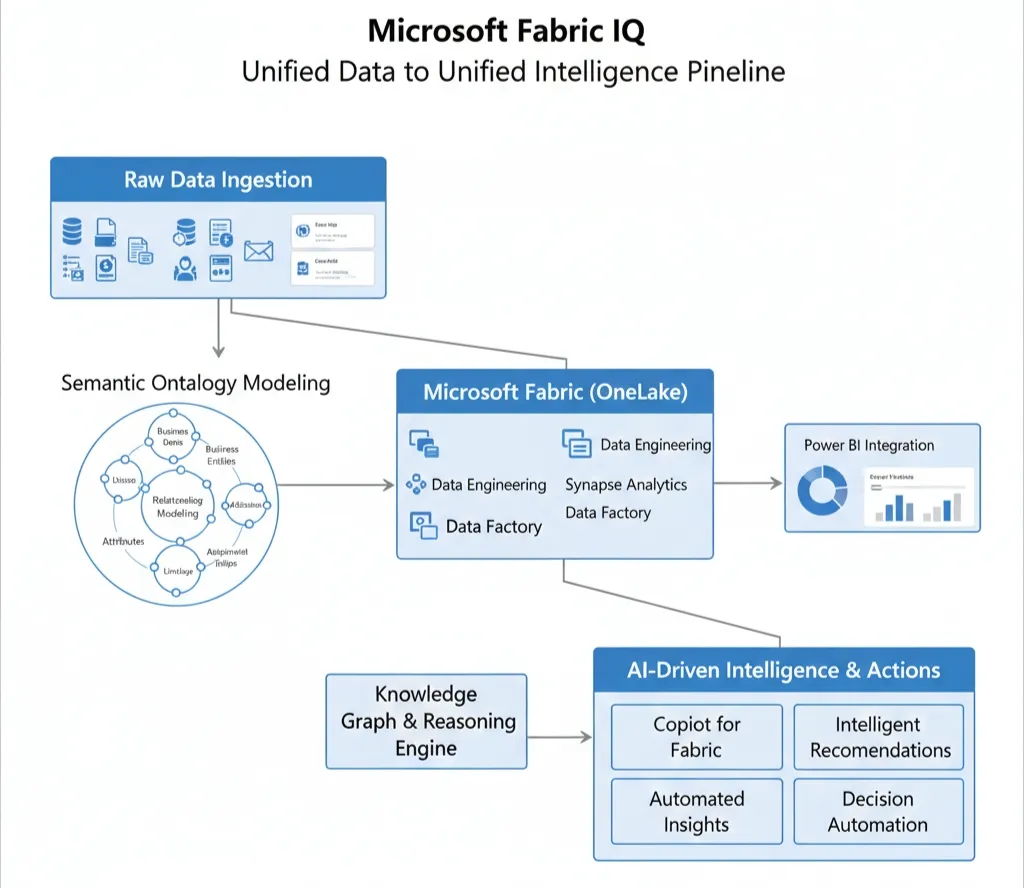
Microsoft Fabric IQ – The Unified Semantic Intelligence Layer
Data forms the backbone of modern AI, but without understanding, data alone cannot drive intelligent action. Enter Microsoft Fabric IQ, the semantic intelligence layer of Microsoft Fabric that unites diverse data, business meaning, and AI-driven operational insights into a single, cohesive model of your organization.
Fabric IQ empowers organizations to model their business in real-time—defining entities, relationships, policies, and automated actions—so everyone from business analysts to autonomous AI agents can work with shared, trusted understanding.
What is Microsoft Fabric IQ?
Microsoft Fabric IQ functions as the unified semantic intelligence layer within Fabric’s data platform, enabling enterprises to define and operate on a shared business model. Instead of users battling raw data tables or incompatible data silos, Fabric IQ creates a business ontology—a formal vocabulary of entities, attributes, relationships, and business logic enriched with full lineage to trusted data sources.
This semantic foundation manifests as a knowledge graph federated across OneLake, Power BI, and real-time event streams. It powers natural language query experiences, AI-powered conversational interfaces, and autonomous operational agents that act contextually on live data.
Why Fabric IQ is Transformational for Enterprises
One of the biggest challenges organizations face is semantic drift—the inconsistent interpretations of business definitions, metrics, and KPIs across departments. Fabric IQ provides a single source of truth, centralizing and certifying these definitions to ensure consistent reporting and decision-making throughout the enterprise.
By embedding policies, business rules, and relationships directly into the semantic framework, Fabric IQ enhances auditability and compliance, accelerates AI adoption by grounding it in trustworthy data, and empowers autonomous business actions.
Core Components of Fabric IQ
- Ontology Authoring (preview): Intuitive no-code visual tools to define and maintain business entities, attributes, relationships, and policies.
- Semantic Knowledge Graph: The backbone linking concepts to live data workflows, creating a unified organizational knowledge model.
- Fabric Data Agent (preview): A natural language conversational bot that leverages ontology semantics to answer complex business queries effortlessly.
- Operations Agent (preview): AI-powered autonomous agents that monitor, reason over, and act on real-time events with full semantic context.
- Graph Engine (preview): A scalable, high-performance graph database facilitating fast retrieval and traversal of the semantic knowledge graph.
- Power BI Semantic Binding: Allowing certified metrics and definitions managed by IQ to be used consistently in Power BI reporting.
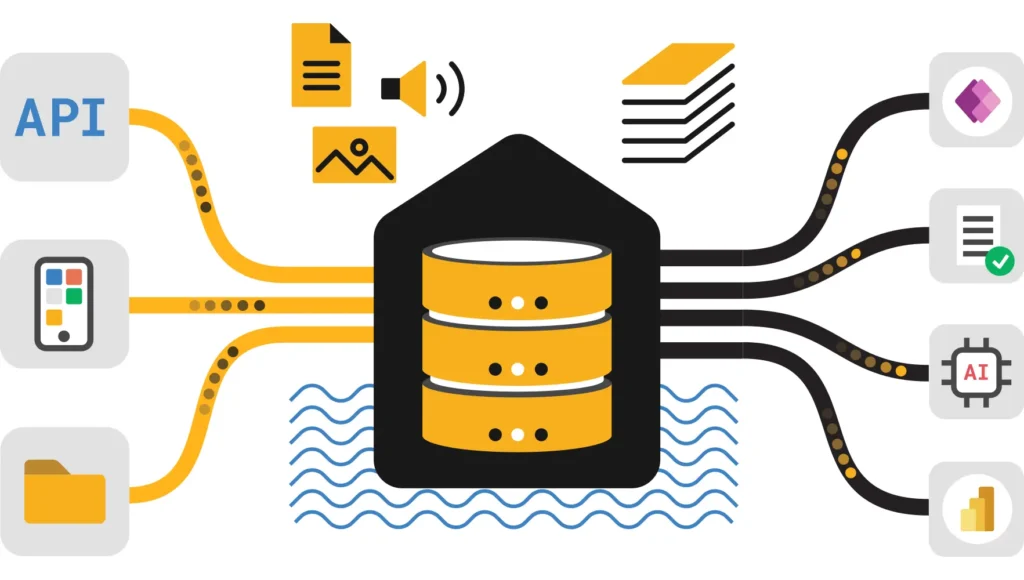
Microsoft Fabric Platform Architecture
This diagram illustrates the unified architecture of Microsoft Fabric integrating OneLake, semantic intelligence, real-time agents, and Power BI visualizations.
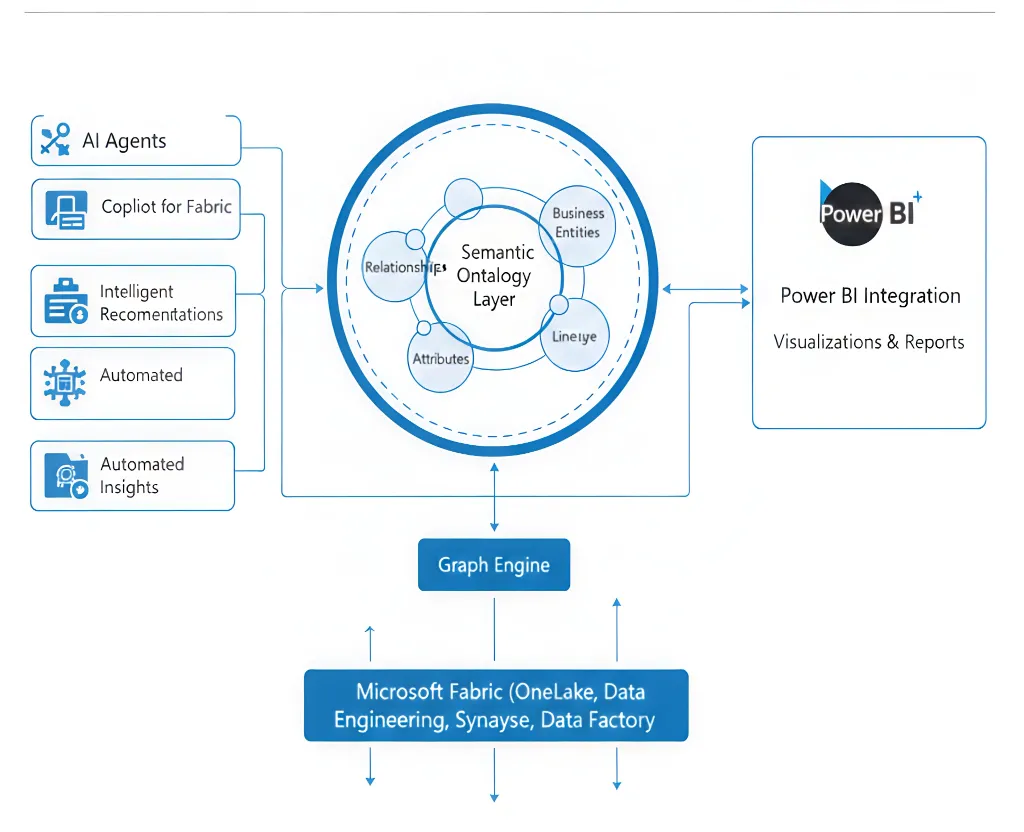
Semantic Ontology – The Semantic Foundation of Fabric IQ
At the heart of Microsoft Fabric IQ is the ontology—a meticulously designed semantic model capturing your organization’s core business concepts. It models entities like customers, products, orders, policies, and more, along with their attributes and interrelationships.
The ontology maps each of these semantic concepts directly to trusted data sets in OneLake, ensuring full traceability and auditability. This enables business analysts, data scientists, and automated AI agents to work with familiar business vocabulary while trusting the underlying data fidelity.
Deep Dive: Ontology and Business Modeling
Ontology entries encompass:
- Entities: Business objects like Customer, Order, Aircraft, or Subscription. Each entity is a semantic stand-in for tables or views but represents concepts intelligible to business users.
- Attributes: Descriptive properties linked to entities, such as Customer Name or Flight Departure Time.
- Relationships: Define how entities associate with each other—e.g., a Customer places many Orders or an Aircraft is assigned multiple flights.
- Business Logic & Rules: Policies, constraints, and computed fields stored directly within the ontology ensure consistent application of business rules across AI and analytics.
- Semantic Lineage & Auditability: Every concept is traceable down to the exact data source, ensuring compliance and trusted interpretations.
This comprehensive semantic scaffolding eliminates inefficiencies caused by data silos or conflicting definitions, accelerating precise AI-driven insights and decision making.
Fabric IQ Ontology Visualization
This image depicts the ontology model within Microsoft Fabric IQ showcasing entities, relationships, and their connection to trusted data assets.
The Fabric Data Agent: Natural Language Query Interface
Business users often struggle with technical query languages or complex BI tools. The Fabric Data Agent solves this by providing a powerful conversational AI interface directly over your semantic model.
This agent understands business questions phrased naturally, maps them to ontology concepts, queries trusted datasets accordingly, and returns accurate, contextually relevant answers instantly.
Operations Agent: Autonomous Decisions Powered by Semantic Intelligence
Operations Agents continuously monitor event streams and data changes, applying the rich semantic context of the ontology. They autonomously detect business-critical conditions and can execute automated remediation actions.
This real-time, AI-powered operational intelligence allows enterprises to reduce downtime, improve reaction times, and maintain high service levels.
Seamless Integration Within Microsoft Fabric Ecosystem
Fabric IQ is tightly integrated with core Fabric workloads, including:
- OneLake: Ontologies map directly to data assets in lakehouses and event streams.
- Power BI: Semantic binding enforces certified metrics and KPIs across reports.
- Real-time agent frameworks: Operations Agents use semantic rules for context-aware workflows.
- AI and automation: Conversational interfaces and automation pipelines leverage Fabric IQ semantics for consistency and governance.
Enterprise Use Cases Empowered by Fabric IQ
- Financial Analytics Consistency: Centralized definitions ensure accurate revenue recognition and financial reporting.
- Operational Autonomy: AI agents autonomously resolve issues, such as technical outages, speeding MTTR.
- Semantic Copilot Experience: Natural language queries help non-technical roles access insights faster.
- Compliance and Auditing: Fully traceable semantic definitions simplify regulatory reporting.
- Cross-Department Collaboration: Shared ontology eliminates report discrepancies and duplicated analysis efforts.
Governance and Safe Rollout Practices
Fabric IQ’s powerful capabilities require strong governance to maintain trust and control:
- Clear Stewardship: Assign dedicated owners for ontology components and mappings.
- Change Approval: Formal workflows to review and approve ontology updates prior to deployment.
- Data Sensitivity Compliance: Leverage OneLake sensitivity labels when exposing ontologies.
- Comprehensive Auditing: Maintain logs of semantic changes and automated decisions.
- Testing & Staging: Use production replicas to validate updates before release.
Getting Started with Microsoft Fabric IQ
- Identify key business domains and the critical concepts to model.
- Map these concepts to your governed OneLake datasets.
- Create and validate ontology entries with domain owners.
- Deploy pilot versions of data and operations agents for real-world testing.
- Iterate based on feedback and expand enterprise-wide rollouts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is Microsoft Fabric IQ generally available yet?
A: Fabric IQ is currently in preview and expanding availability. Check Microsoft Fabric official updates for latest info.
Q: Can Fabric IQ use external data sources?
A: It primarily operates over OneLake data; external data should be ingested or replicated into OneLake for integrated semantics.
Q: Will Fabric IQ replace existing semantic models?
A: It complements and centralizes governance of models; existing Power BI or other models bind to IQ-managed definitions.