Eventstream in Fabric – Complete 2026 Guide
Master real-time event ingestion, transformations, and routing with official Microsoft documentation. Build production-grade streaming analytics without code.
Updated January 2026What is Eventstream in Fabric?
Eventstream in Fabric is a no-code, real-time analytics service that enables you to capture, transform, and route data events from sources like Azure Event Hubs, Kafka, and IoT devices directly into Fabric destinations. As of January 2026, it features Direct Ingestion for ultra-low latency and enhanced real-time hubs for unified stream management.
Eventstream in Microsoft Fabric represents a managed, no-code service for capturing, transforming, and routing real-time events from diverse sources (Event Hubs, Kafka, IoT Hub, HTTP) to destinations (Eventhouse, Lakehouse, Service Bus, webhooks). Notably, January 2026 brings Direct Ingestion to Eventhouse, enhanced event processors, and tighter integration with Real-Time Hub. Throughout this guide, you’ll discover every capability paired with production patterns that scale.
Table of Contents
- What is Eventstream in Fabric
- Core Capabilities & Use Cases
- Architecture: Sources, Processors, Sinks
- Direct Ingestion vs Event Processing
- Event Processors & Transformations
- Sources: Event Hubs, Kafka, IoT, HTTP
- Destinations: Eventhouse, Lakehouse, Custom
- Temporal Windowing & Aggregations
- Design Patterns & Real-World Recipes
- Performance, Scaling & Cost Control
- Monitoring, Security & Observability
- Best Practices for Production
- Official Documentation & References
What is Eventstream in Fabric?
Eventstream represents Microsoft Fabric’s real-time data ingestion and transformation service. Fundamentally, it captures events from multiple sources, applies lightweight transformations (filtering, enrichment, aggregation), and routes results to Fabric analytics destinations or external systems. All of this operates without writing code—fully managed infrastructure scales automatically to meet demand.
💡 Thinking about starting a small side income online?
Many creators start with simple tools and workflows — no investment required.
See how creators do it → CreatorOpsMatrix.comJanuary 2026 Highlights
Direct Ingestion to Eventhouse (GA): Stream events directly to KQL databases without intermediate processing. Enhanced Event Processors: Richer transformations include temporal windowing, joins, and field management. Real-Time Hub Integration: Discover and manage all streaming artifacts from a centralized hub. Derived Streams: Chain eventstreams for complex topologies and improved reusability.
Core Capabilities & Use Cases
In practice, Eventstream excels at handling diverse real-time scenarios. Consider these four primary capabilities:
Ingest Real-Time Events
Leveraging 140+ event sources: Event Hubs, Kafka, IoT Hub, HTTP endpoints, Service Bus. Handle millions of events per second effortlessly.
Transform Lightweight
Additionally, filter, enrich, aggregate, join, and group by time windows. Apply all transformations with minimal latency impact.
Route Flexibly
Furthermore, route to multiple sinks simultaneously: Eventhouse (new!), Lakehouse Delta, Service Bus, Event Hub, webhooks, and custom endpoints.
No-Code Experience
Ultimately, the drag-and-drop UI with pre-built processors enables professional streaming analytics without custom code development.
When to Use Eventstream
Understanding the right use cases helps maximize Eventstream’s value across your organization:
- Real-Time Dashboards: Clickstream analytics, user activity, operational metrics—refresh KQL dashboards per second for immediate insights
- Alerting Pipelines: Threshold breaches, anomaly detection, SLA violations—trigger actions immediately upon detection
- Feature Generation for ML: Compute streaming aggregates (user lifetime value, engagement scores) for ML models with current data
- Event Archival: Capture all events to OneLake for audit, compliance, and batch analytics on historical data
- Real-Time ETL: Enrich source events with reference data and route to downstream systems seamlessly
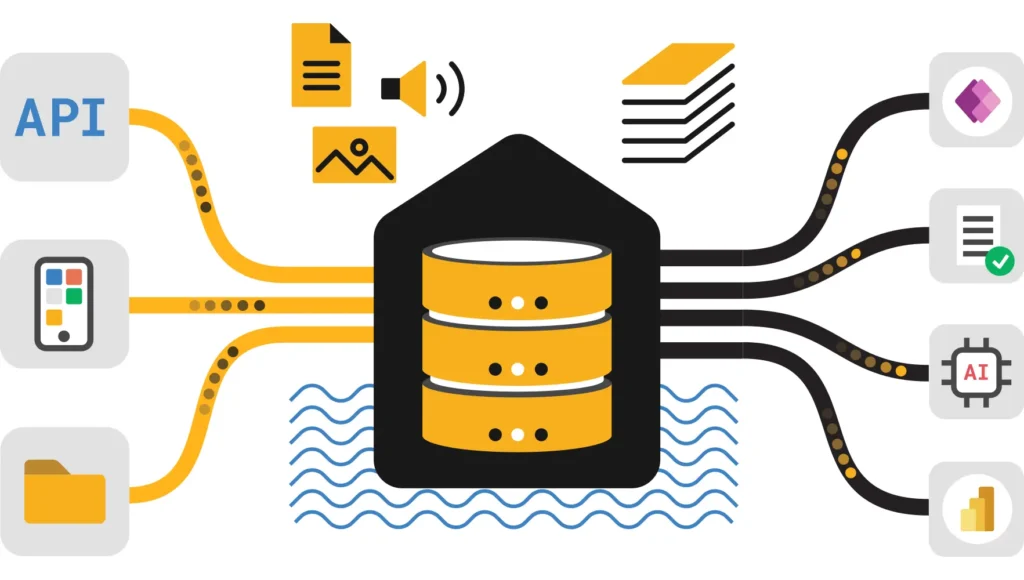
Architecture: Sources → Processors → Destinations
Essentially, every Eventstream follows a three-stage pipeline design. Understanding this flow enables better architectural decisions:
[Event Sources] → [Default Stream] → [Transformations] → [Destinations]
Sources (pick one or more):
• Event Hub (high-volume real-time events)
• Kafka (on-premises or cloud clusters)
• IoT Hub (device telemetry data streams)
• HTTP Custom Endpoint (webhooks from SaaS, applications)
• Service Bus (enterprise messaging infrastructure)
Transformations (optional, pick multiple):
• Filter (WHERE clauses for event selection)
• Aggregate (SUM, AVG, COUNT over time windows)
• Group By (with temporal windows: tumbling, hopping, session, sliding)
• Join (enrich from lookup streams)
• Manage Fields (rename, type cast, add computed columns)
Destinations (route to one or more):
• Eventhouse (KQL database) – NEW Direct Ingestion mode
• Lakehouse (Delta tables in OneLake)
• Event Hub (fan-out to subscribers)
• Service Bus (decouple consumers)
• Custom Endpoint (Kafka, AMQP, HTTP webhooks)
• Derived Stream (chain eventstreams)
Direct Ingestion vs Event Processing Mode
Choosing the right ingestion strategy depends on your requirements. Here are the two primary approaches:
Direct Ingestion (Recommended)
Available (NEW Jan 2026): Stream events directly to KQL database without intermediate processing. Ideal for high-throughput scenarios where raw data storage takes priority.
• Archive all events as-is for compliance
• Minimize latency—no transformation overhead
• Perform analytics later via KQL
• Handle variable schemas
Event Processing Before Ingestion
Apply transformations (filter, aggregate, enrich) before data lands. Reduces storage and focuses on processed insights.
Pattern: Direct Ingestion → Real-time KQL dashboards (queries run on freshly ingested data). Additionally, maintain a separate batch layer for curated, enriched views.
Event Processors & Transformations
Eventstream supports six core transformation types. Chaining them together builds complex processing logic without code.
Filter
Select events matching specific conditions. For instance, keep only transactions over $100 or errors from production environments.
Aggregate
Compute SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX across time windows. Notably, calculate per-minute order totals or hourly user activity metrics.
Group By
Segment events by dimension (region, product category). Furthermore, combine with temporal windows for time-series aggregations.
Join
Enrich event streams with reference data. Additionally, correlate events from multiple sources for comprehensive insights.
Manage Fields
Rename, type-cast, or compute new columns. Moreover, rename fields for downstream compatibility and add derived metrics.
Convert
Transform data between formats. Additionally, convert event types or change field representations for different sink requirements.
Building a Transformation Pipeline
Importantly, transformation pipelines follow a logical sequence. Consider this real-world example:
1. Raw Source: Orders from Event Hub (many formats, incomplete data)
2. Filter → Keep only orders > $50
3. Manage Fields → Rename “OrderID” to “order_id”, cast price to decimal
4. Join → Lookup customer region, product category from reference tables
5. Aggregate → Calculate COUNT and SUM(price) per region, per minute
6. Destination → Send aggregated metrics to Eventhouse for BI dashboards
Sources: Event Hubs, Kafka, IoT, HTTP
Choosing the right source depends on your data origin and connectivity. Here are the primary options:
Event Hub (Azure)
Azure’s managed event streaming service, handling millions of events per second. Perfect for high-throughput cloud-native architectures.
Apache Kafka
Open-source distributed streaming platform, widely adopted in enterprises. Supports both cloud and on-premises deployments.
IoT Hub
Azure IoT Hub provides device-to-cloud messaging with device management capabilities. Ideal for IoT solutions with thousands of devices.
HTTP Custom Endpoint
Receive events via HTTP webhooks. Perfect for SaaS platforms, mobile apps, and third-party integrations pushing data.
Destinations: Eventhouse, Lakehouse, Custom
After transformation, data travels to one or more destinations. The choice depends on use case and downstream consumers:
| Destination | Best For | Latency | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eventhouse (KQL) | Real-time dashboards, alerting | Sub-second | Medium |
| Lakehouse (Delta) | Data lake storage, batch analytics | Secs/Mins | Low |
| Event Hub | Fan-out to multiple subscribers | Sub-second | Medium |
| Service Bus | Guaranteed delivery, messaging | Millisecs | Medium/High |
| Custom Endpoint | External systems, 3rd party | Variable | Variable |
Temporal Windowing & Aggregations
Windowing enables time-based analytics on infinite streams. Understanding window types is crucial for accurate metrics:
1. Tumbling Window
Non-overlapping fixed intervals (e.g., 1-minute windows). Each event belongs to exactly one window. Perfect for per-minute aggregations like order count, revenue total.
2. Hopping Window
Overlapping fixed intervals (e.g., 5-minute window, advancing every 1 minute). Provides smoothed metrics. Useful for moving averages and trend detection.
3. Session Window
Dynamic duration based on gaps between events. Perfect for user sessions: consecutive events close in time belong to same window, gaps trigger new window.
4. Sliding Window
Continuously advancing fixed-duration window. Every new event creates new window. Most precise for real-time anomaly detection.
Windowing Example: E-Commerce Metrics
Tumbling (1 min): COUNT(orders), SUM(price) per 1-min bucket
Result: At 10:00 AM, 45 orders totaling $2,340
Hopping (5 min, hop 1 min): Moving average of order count
Result: Smooth trend showing traffic peaks at specific times
Session (30 sec gap): Group consecutive user events into sessions
Result: Each visitor session tracked separately for behavior analysis
Design Patterns & Real-World Recipes
Implementing Eventstream effectively requires proven architectural patterns. Here are three essential patterns:
Lambda Architecture: Speed + Serving Layers
Combine fast real-time processing with slower but comprehensive batch processing.
Speed Layer: Raw events → Direct Ingestion to Eventhouse → KQL dashboard (updated per second)
Batch Layer: Raw events → Lakehouse → Dataflow (enrichment, complex joins) → Curated tables (daily)
Serving Layer: KQL for immediate metrics + Delta tables for deep analysis
Event Sourcing: Immutable Log Pattern
Treat Lakehouse as immutable append-only log. All events stored permanently; analytics queries scan relevant subsets.
All events → Direct Ingestion to Lakehouse (immutable archive)
Queries filter by timestamp, region, event type as needed
Enables audit trails, replay-able processing, and compliance
Fanout Pattern: Multi-Destination Routing
Single Eventstream routes processed events to multiple destinations based on content.
Raw events → Filter by severity (ERROR, WARNING, INFO)
ERROR events → Service Bus (triggers alert automation)
All events → Lakehouse (audit log)
Aggregated metrics → Eventhouse (dashboards)
Performance, Scaling & Cost Control
Production-grade Eventstream requires attention to performance metrics and costs. Consider these optimization strategies:
Throughput Optimization
- Event Hub Partitioning: Distribute events across partitions by customer ID or region. Eventstream processes partitions in parallel.
- Batch Windows: Aggregate within Eventstream before sending to destination. Reduces downstream volume by 10-100x.
- Compression: Enable compression for Event Hub and Kafka sources to reduce bandwidth.
- Parallel Processors: Run multiple Eventstream instances on different partitions for linear scaling.
Cost Management
- Direct Ingestion (January 2026): Ingestion units cost less than traditional event processing paths.
- Filtering Early: Remove unwanted events at source. Don’t store unnecessary data to Lakehouse.
- Windowing Aggregation: Reduce event volume 100x by pre-aggregating in Eventstream vs storing raw.
- Retention Policies: Set TTL (time-to-live) on Lakehouse data; archive old events to cold storage after 90 days.
Monitoring, Security & Observability
Operating reliable Eventstreams in production demands robust monitoring and security practices.
Monitoring & Alerting
- Eventstream Metrics: Monitor latency, throughput, error rate, pending event count in Monitor Hub
- KQL Queries: Write queries on eventhouse tables to track data quality (null rates, duplicates, schema drift)
- Data Validation: Aggregate checks in Eventstream: count distinct users, detect outlier values
- Alerting Rules: Set up KQL alerts: if error rate > 5% or latency > 10 sec, page on-call team
Security Best Practices
- Authentication: Use Managed Identity for Eventstream → Eventhouse/Lakehouse connections. No credential management.
- Encryption: Enable TLS for all data in transit. Use Lakehouse encryption at rest (automatic).
- Access Control: Assign Workspace roles: Contributor for developers, Member for limited access
- PII Handling: Mask sensitive fields in Eventstream transformations before storing to Lakehouse
Best Practices for Production
Design & Architecture
- Schema Registry: Define event schemas upfront (Avro, JSON Schema). Validate incoming events; reject non-conforming.
- Partition Strategy: Partition by high-cardinality dimension (customer ID, device ID) for balanced throughput.
- Derive Streams: Chain Eventstreams for reusability. One raw stream → multiple derived streams (error filter, metrics aggregation).
- Capacity Planning: Estimate peak events/sec. Overprovision Event Hub by 2-3x for spike tolerance.
Data Quality
- Deduplication: Use event ID to detect and skip duplicate messages (idempotent processing).
- Late Arrivals: Accept events arriving seconds/minutes late. Use processing time, not event time, for real-time dashboards.
- Watermarking: Track maximum event timestamp processed. Detect gaps indicating data loss.
- Schema Evolution: Plan for field additions without breaking existing queries. Use optional fields.
Operations & Troubleshooting
- Backpressure Handling: If Eventhouse ingestion lags, Eventstream queues events. Monitor queue depth; scale up Eventhouse if needed.
- Replay Capability: Store raw events to Lakehouse with timestamps. Replay through Eventstream for reprocessing if transformation logic changes.
- Diagnostic Queries: Run KQL queries to compare source counts (Event Hub) vs sink counts (Eventhouse). Detect loss.
- Scaling Patterns: Horizontal scaling: add Event Hub partitions, add Eventstream consumers per partition.
Official Documentation & References
Core Microsoft Fabric Documentation
- Eventstream Overview (Official) – Complete reference for all capabilities and features.
- Add Event Hub Source – Step-by-step Event Hub integration.
- Add Kafka Source – Configure Apache Kafka connectors.
- Add Eventhouse Destination – Direct ingestion to KQL database (January 2026).
Advanced Guides & Tutorials
- Real-Time Analytics in Fabric (KQL Databases) – Deep dive into KQL queries and dashboarding.
- Eventstream Tutorials 2026 – Hands-on examples and use-case implementations.
- Data Pipelines in Fabric – Orchestrate Eventstream outputs with batch processing.
- Fabric Capacity Optimization – Right-size compute for streaming workloads.
Related Fabric Capabilities
- Lakehouse in Fabric – Delta Lake storage for archived events.
- KQL Database (Eventhouse) – Real-time analytics engine for time-series data.
- Real-Time Hub in Fabric – Unified discovery of streaming artifacts.
- Fabric Pricing Calculator – Estimate costs for streaming workloads.
2026 Innovation Roadmap
Direct Ingestion (GA Jan 2026): Stream directly to Eventhouse without processing overhead. Enhanced Processors (Jan 2026): Temporal windowing, streaming joins, field management improvements. Real-Time Hub (GA): Centralized discovery and management of all streaming artifacts across the workspace. Derived Streams (Preview): Chain eventstreams for composable architectures and better reusability.
Ready to Build Real-Time Analytics?
Start by building your first Eventstream: connect an Event Hub source, add a simple filter transformation, and route to Eventhouse. Monitor the data in Monitor Hub. Subsequently, build a KQL dashboard to visualize metrics in real-time. As your confidence grows, layer in aggregations, joins, and multiple destinations. Finally, implement retry logic, schema validation, and cost controls for production workloads.
Questions? Explore the official Eventstream documentation, dive deeper into tutorials, or learn about KQL databases for analytics.
Frequently Asked Questions (2026 Update)
What is the difference between Eventstream and Event Hubs?
Azure Event Hubs is the underlying transport layer (the pipe). Fabric Eventstream is the no-code orchestration tool that consumes from Event Hubs, transforms the data (filters, joins), and routes it to destinations like the Lakehouse or Eventhouse.
Does Direct Ingestion cost more than Event Processing?
No, typically Direct Ingestion costs less because it bypasses the compute-intensive transformation processing units. However, you store more data (raw events) in the destination, so storage costs may slightly increase compared to storing only aggregated data.
Can Eventstream handle duplicates?
Eventstream itself provides “at-least-once” delivery guarantees. To handle duplicates, it is best practice to use the Direct Ingestion mode into a KQL Database (Eventhouse) and use KQL’s ingest_if_not_exists tags or deduplicate at query time using the arg_max() function.
Is Eventstream available in Fabric Trial capacities?
Yes, Eventstream is fully available in Fabric Trials. However, for production workloads exceeding the trial limits (CU usage), you should migrate to an F-SKU (F2 or higher) to ensure consistent throughput.