Data Pipelines in Fabric – Complete 2026 Guide
Updated: January 2026 | Category: Data Engineering
Optimize Your Tech Career & Business: Managing Fabric capacity and complex pipelines is demanding. Ensure your income matches your expertise or calculate the impact of Fabric pricing on your budget.
What are Data Pipelines in Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric Data Pipelines act as the central orchestration engine for modern cloud analytics. They allow engineers to build low-code ETL workflows that move data from over 90 sources, perform complex transformations using Spark or SQL, and automate business logic via flexible triggers. As of January 2026, they serve as the unified, enterprise-grade successor to Azure Data Factory within the Fabric ecosystem.
Microsoft Fabric Data Pipelines form the backbone of modern data orchestration. Whether you are building simple ETL workflows, orchestrating massive Spark jobs, or implementing event-driven architectures, this comprehensive guide covers every activity, trigger type, and best practice for production-grade pipelines in 2026.
💡 Thinking about starting a small side income online?
Many creators start with simple tools and workflows — no investment required.
See how creators do it → CreatorOpsMatrix.comTable of Contents
- Introduction to Fabric Pipelines
- Trigger Types: Complete Reference
- Copy Activity & Copy Job
- Dataflow Activity & Parameters
- Execute Pipeline (Invoke)
- Lookup Activity
- ForEach Activity
- Control Flow Activities
- Web & WebHook Activities
- Spark & Notebook Activities
- Stored Procedure Activity
- Monitoring & Security
- Best Practices 2026
Introduction to Data Pipelines in Fabric
Microsoft Fabric Pipelines (formerly known simply as “Data Pipelines”) provide cloud-scale orchestration for data movement, transformation, and business logic. Fundamentally, pipelines consist of activities (the building blocks), control flow (such as conditionals and loops), and triggers (the logic dictating when to execute).
Before diving into the specifics, it is helpful to understand how pipelines fit into the broader Microsoft Fabric Overview. Unlike older tools, Fabric pipelines are deeply integrated with OneLake, allowing for seamless data movement between Lakehouses, Warehouses, and external sources.
[attachment_0](attachment)What’s New in January 2026?
Service Principal Support
Run notebooks with workspace identity or service principals for hardened production workloads. This eliminates dependency on individual user accounts.
Expanded CDC Coverage
The new Copy Job now supports change data capture for SAP, Snowflake, and BigQuery sources, making real-time replication easier.
Copilot Expression Builder
You can now use natural language to generate pipeline expressions and debug errors with AI assistance, significantly speeding up development.
Trigger Types for Data Pipelines in Fabric
Pipelines can be triggered automatically via schedules and events, or they can be run on-demand. Choosing the right trigger strategy is essential because it ensures efficient resource use and timely data delivery. Moreover, improper triggering can lead to capacity throttling.
| Trigger Type | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Trigger | Run on demand via UI or REST API. | Ad-hoc operations, testing, and debugging. |
| Schedule Trigger | Recurrence-based: hourly, daily, weekly, monthly. Supports up to 20 schedules per pipeline. | Time-based ETL and maintenance jobs. |
| Event Trigger | File arrival, file deletion, OneLake folder events. | Event-driven architecture for reactive workflows. |
| Job Event Trigger | Trigger pipelines when parent jobs complete. | Essential for dependent pipeline orchestration. |
Schedule Trigger Deep Dive
You should use schedule triggers for time-based ETL, incremental loads, and maintenance jobs. Furthermore, you can configure them with timezone support and multiple time windows. This flexibility allows for complex scheduling without needing external schedulers.
Example configurations include:
- Every 10 minutes starting at 6:00 AM
- Every 2 hours (2:00 AM, 4:00 AM, 6:00 AM, …)
- Daily at specific times (e.g., 6:00 AM and 2:00 PM)
- Weekly on Monday-Friday at 9:00 AM
Event Trigger Implementation
Event triggers respond to file system changes and job completions without polling. This leads to lower latency and reduced costs compared to schedule-based polling.
- File Arrival Event: Trigger a pipeline when CSV files appear in a OneLake folder. This uses the blob trigger pattern, which is perfect for real-time ingestion. Learn more about Eventstream in Fabric for real-time needs.
- Job Completion Event: When a parent dataflow or lakehouse refresh completes, the child pipeline auto-runs. Consequently, you can build dependent workflows without manual handoff.
- Monitor & Debug: Use the Monitor Hub to see which trigger fired each pipeline run (manual, schedule, or event). This is critical for auditing and troubleshooting.
Copy Activity & Copy Job (NEW)
Understanding the difference between the standard Copy Activity and the newer Copy Job is vital for modern pipeline design. While they share similar goals, their implementation details differ significantly.
Copy Activity vs Copy Job
Copy Activity
Use for: Low-code data movement in pipelines. It connects to 90+ sources (Azure, AWS, on-premises). It supports batch processing, incremental loads with watermarking, and traditional Change Data Capture (CDC).
Copy Job (Nov 2025)
Use for: No-code pipeline activities. Leverage existing or create new Copy Jobs directly within orchestration. Features include truncate before full load and query-based incremental copies.
Real-World Use Case: Imagine you need to copy hourly CSV exports from Azure Blob Storage to a Lakehouse as Delta tables. You can configure the Copy Activity to skip rows with type mismatches, log failures to an audit table, and retry 3 times on timeout.
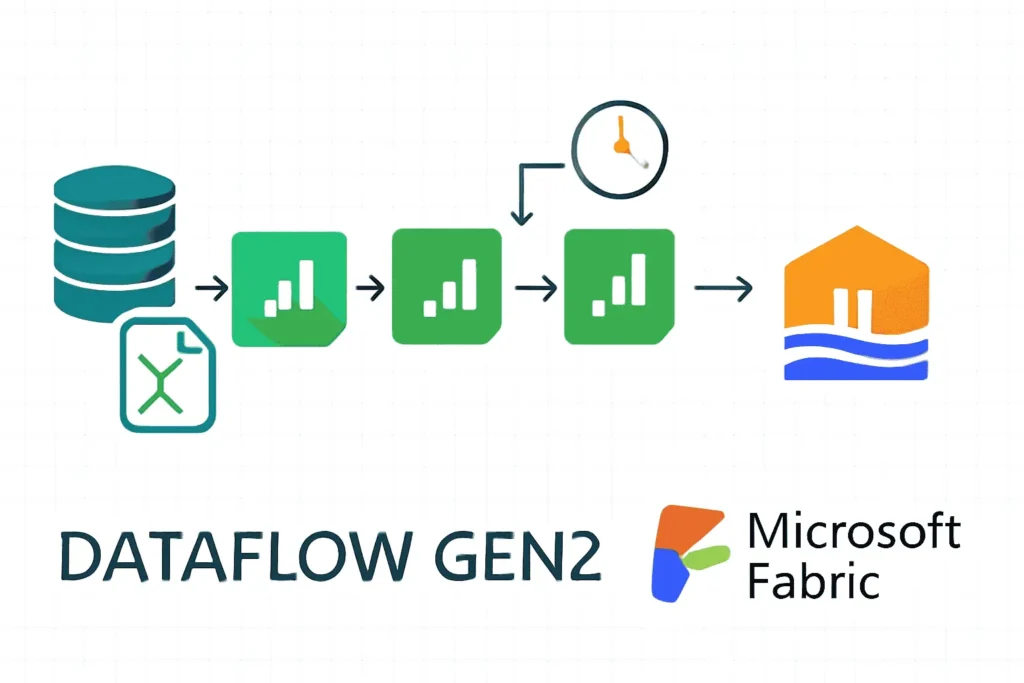
Dataflow Activity: Visual Transformations
The Dataflow Gen2 in Fabric allows for managed Spark cluster execution with a low-code visual design. It handles joins, filters, aggregations, and schema drift handling with ease.
Parameters (2026 Feature)
Parameters significantly enhance the flexibility of your dataflows. Specifically, they offer:
- Dynamic Inputs: Pass parameters from pipeline variables to dataflow connectors.
- Filter Push-down: Apply
WHEREclauses from parameters before data loads. - Reusability: Use one dataflow with many parameter combinations across workflows.
Parameterized Dataflow Example: A Dataflow accepts a @param_date parameter. The Pipeline sets param_date from a Lookup activity (latest load date). Finally, the Dataflow filters source data WHERE load_date > @param_date to achieve incremental transformation without hardcoding dates.
Execute Pipeline (Invoke Pipeline)
The Execute Pipeline activity allows you to invoke child pipelines from parent pipelines. This promotes modular architecture where you can pass parameters, wait for completion, and handle errors modularly.
Key features as of 2026 include:
- Service Principal Support: Execute pipelines with workspace identity or service principal authentication.
- VNet Gateway Support: Seamless integration with On-premises and VNet data gateways.
- Parameter Passing: Input parameters flow to the child pipeline, which processes them and outputs back to the parent.
Lookup Activity: Data-Driven Logic
Use the Lookup Activity to retrieve configuration, parameters, or data lists from databases, REST APIs, or files. Subsequently, use these results to conditionally control pipeline flow.
Lookup Pattern: Incremental Load
One of the most common uses for Lookup is managing incremental loads. Here is a step-by-step implementation:
- Lookup Activity: Query a control table in your warehouse:
SELECT MAX(last_load_date) FROM LoadLog WHERE table_name = 'Customers' - Copy Activity: Use the lookup output as a dynamic parameter in your source query:
WHERE modified_date > '@{activity('LookupLastLoad').output.firstRow.last_load_date}' - Stored Procedure Activity: After the copy succeeds, update the control table:
EXEC sp_UpdateLoadLog @table_name='Customers', @load_date=GETUTC()
Result: Only changed data is loaded, and an audit trail is maintained. This ensures your Fabric Lakehouse vs Data Warehouse strategy remains efficient.
ForEach Activity: Batch Processing
The ForEach activity executes a set of activities for each item in an array. It supports both sequential and parallel execution modes, which is critical for performance tuning.
ForEach + Lookup: Batch Pattern
This pattern is essential for processing multiple files or partitions dynamically.
Step 1: Lookup → Fetch list of files to process
Query: SELECT file_id, file_path FROM FileQueue WHERE status = 'pending'
Step 2: ForEach → Iterate over lookup output
Expression: @activity('LookupFiles').output.value
Step 3: Inside ForEach → Copy/Transform individual file
Source Path: @item().file_pathParallelization: Set “Parallel execution” to true for independent items (default is 20 concurrent). This is significantly faster for large file batches. However, use sequential mode if the order of operations matters, such as when applying sequential updates to a database.
Control Flow Activities in Data Pipelines
Beyond simple loops, advanced control flow activities allow you to build sophisticated logic directly within the orchestration layer.
If Condition Activity
This activity evaluates a boolean expression and executes either the true branch or false branch activities. Common expressions include:
@equals(dayofweek(utcnow()), 1)→ Returns True on Sunday.@greater(activity('LookupRowCount').output.firstRow.row_count, 1000)→ Checks if rows exceed 1000.
Switch Activity
Use the Switch activity for multi-way branching. It evaluates a selector expression against multiple cases, which is cleaner than nested If conditions.
Switch Pattern: Selector Expression: @activity('GetFileMetadata').output.firstRow.file_type
- Case 1: “CSV” → Copy Activity for CSV mapping
- Case 2: “JSON” → Dataflow for JSON transformation
- Default: → Log error, skip file
Until Activity
The Until activity repeatedly executes inner activities until a condition is met. This is particularly useful for polling external status or retry logic, such as waiting for an external API to return a “Completed” status before proceeding.
Web & WebHook Activities
Web Activity
Send HTTP requests (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to REST endpoints. You can call microservices, fetch data, or trigger external workflows. This connects Fabric to the rest of your IT ecosystem.
Real Example: REST API Token Auth
- Web Activity POST login request (email/password in body).
- Extract token:
@activity('GetToken').output.data.token. - Set Variable with token.
- Copy Activity uses token in Authorization header to fetch protected data.
WebHook Activity
Conversely, the WebHook Activity calls an endpoint and waits for a callback. Pipeline execution pauses until the webhook receiver invokes the callback URL. This effectively enables async workflows, such as waiting for human approvals or long-running external processes.
Spark & Notebook Activities
Execute Spark notebooks with workspace identity or service principal authentication. This approach hardens production workloads by removing user-bound sessions. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on Transforming Data Using Notebooks.
New Feature: Service Principal Execution
As of December 2025, executing notebooks via Service Principals is the gold standard for production.
- Non-Interactive Runs: Notebooks run with Entra ID service principal credentials, not user context.
- Production-Grade Security: No user session is required; credential rotation is handled via Azure Key Vault.
- Audit Trail: All notebook execution is logged under the service principal identity, simplifying compliance audits.
If you encounter performance issues with small files during Spark jobs, refer to our Spark Shuffle Partitions Optimization guide.
Stored Procedure Activity
Call database stored procedures on Fabric SQL DB, Azure SQL, or Synapse SQL. This allows you to execute complex business logic close to the data, minimizing data movement.
When to Use Stored Procedure vs Lookup: Use a Stored Procedure when you need to modify state (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) and don’t need to capture output. In contrast, use Lookup when you need to retrieve data for downstream decisions.
Monitoring, Security & Error Handling
Pipeline Monitoring Best Practices
Effective monitoring is the difference between a fragile pipeline and a robust data platform.
- Monitor Hub: View all pipeline runs and filter by status or trigger type. Drill down into activity-level details to see failures.
- Activity Logs: Copy Activity logs show row counts and skipped rows. Dataflow logs show Spark job performance.
- Capacity Monitoring: Track pipeline CU (Capacity Unit) consumption. If heavy transformations occur during peak hours, consider optimizing Microsoft Fabric Capacity.
- Copilot Error Insights: AI-powered error explanation surfaces root causes and recommends fixes without manual debugging.
Security Checklist
- ✅ Never hardcode credentials in pipelines. Use Linked Services + Key Vault.
- ✅ Use Service Principals: assign them to the Workspace with minimal roles (Contributor).
- ✅ Audit all pipeline runs via Monitor Hub.
- ✅ Review Cloud Security Tips for broader environment hardening.
For more on governance, read our Fabric Data Governance Tutorial.
Best Practices for Data Pipelines in Fabric in 2026
To build resilient and scalable pipelines, follow these industry-proven strategies.
Modularity
Use Execute Pipeline to break large workflows into reusable child pipelines. This makes it easier to test, debug, and reuse logic across different projects.
Parameterization
Define pipeline parameters for environment-specific values (e.g., server names, file paths). This promotes code reuse across Dev, QA, and Prod environments.
Variable Library
Store variables in a centralized Variable Library. This simplifies multi-pipeline orchestration and environment-specific values.
Real-World Scenario: Multi-Tenant Data Pipeline
Imagine you manage a SaaS platform with 100 customers. Each customer has daily data in Blob Storage, and you need to load them into separate Lakehouse tables. A linear approach would be too slow.
Pipeline Architecture (2026 Recommended Approach)
Parent Pipeline: "Orchestrate Daily Loads"
1. Lookup → Fetch list of active customers from config table
2. Set Variable: @variables('error_messages') = [empty array]
3. ForEach customer (parallel, 20 concurrent):
→ Invoke Child Pipeline ("Process Customer Data") with @item().customer_id
→ On failure: Append to error_messages array
4. If @variables('error_messages').length > 0:
→ Email Activity: Send failure summary
→ Else: Stored Procedure (mark daily load successful)
5. Dataflow Activity: Aggregate metrics across all customersWhy This Design?
- Modularity: The child pipeline is reusable for ad-hoc customer loads.
- Parallelization: 100 customers are processed in parallel (20 at a time), reducing total runtime.
- Error Resilience: One customer failure doesn’t block others from completing.
Additional Essential Activities
Beyond the core data movement tasks, robust pipelines require utility activities to manage state, clean up resources, and handle logic flow effectively.
User Data Functions (UDF) Activity
New in the 2026 update, this activity allows you to call custom Python functions directly from pipelines. This bridges the gap between low-code orchestration and high-code business logic without the overhead of a full Notebook.
- Develop Mode: Test functions interactively before publishing them to the pipeline.
- Async Support: Native support for non-blocking function calls, perfect for lightweight data parsing using pandas.
- Use Case: Use UDFs for complex string manipulation or custom encryption logic that is difficult to implement in standard expression language.
Delete Activity
This activity removes files or folders from your Lakehouse or cloud storage. It is critical for cleanup and storage cost management.
Use Case: After successfully processing a daily CSV file, use the Delete Activity to remove it from the “Staging” folder. Alternatively, if a pipeline fails, use it to delete partial results to ensure a clean retry.
Set Variable & Append Variable
Managing state within a pipeline run is essential for complex logic.
- Set Variable: Initialize or update a pipeline variable value (e.g.,
@variables('error_count').value = 0). - Append Variable: Add elements to an array dynamically. For example, inside a ForEach loop, you can append the name of every processed file to a
@variables('processed_files')array for final reporting.
Wait & Fail Activities
- Wait Activity: Pauses pipeline execution for a specified duration. This is useful for rate limiting when calling external APIs (e.g., waiting 60 seconds between calls).
- Fail Activity: Intentionally terminates the pipeline with a custom error message. Use this for validation: “If row_count < 100, trigger Fail Activity with message 'Data Quality Threshold Breached'."
Advanced Troubleshooting & Common Errors
Even well-architected pipelines encounter issues. Here is how to resolve common 2026 era errors.
1. 403 Forbidden / Authorization Errors
This is the most common error when connecting to storage or external APIs. It usually stems from missing Service Principal permissions.
- Fix: Ensure the Service Principal is assigned the “Contributor” role on the specific OneLake item or Storage Account.
- Context: If you are orchestrating external container workloads, you might face similar issues. See our guide on Airflow Kubernetes Operator 403 Fixes for parallel concepts in orchestration.
2. “Column Not Found” or Data Mismatches
Schema drift often breaks Copy Activities. If a source column is renamed or missing, the pipeline will fail.
- Fix: Use the “Get Metadata” activity to validate the column list before running the Copy Activity.
- Deep Dive: If you are struggling with PySpark errors during these transformations, check our Py4JJavaError Saving Delta Table Fix.
3. Direct Lake & Performance Issues
Pipelines loading data into the Warehouse/Lakehouse must be optimized for Direct Lake mode to ensure Power BI reports remain fast.
- Optimization: Ensure you are not creating too many small files (the “small file problem”). Compact your tables after loading.
- Reference: Read our guide on DP-600 Direct Lake Optimization and Direct Lake Fallback Fixes to prevent reporting lag.
Integration with dbt and External Tools
Microsoft Fabric pipelines do not exist in a vacuum. In 2026, they tightly integrate with modern data engineering standards.
dbt (Data Build Tool) Integration
While Fabric Dataflows are great for visual transformations, many engineering teams prefer SQL-based transformations using dbt.
- Pattern: Use Fabric Pipelines to extract and load data (EL), then trigger a dbt job to perform the transformation (T).
- Resource: Learn more about structuring these projects in our dbt Best Practices Guide.
2026 Pipeline Innovation Highlights
To wrap up, here are the cutting-edge features that set Fabric apart this year:
dbt Job Activity
Natively author and schedule dbt projects with serverless execution, integrated testing, and Entra ID security directly within the pipeline canvas.
AI Agents
Move beyond simple orchestration. New Agentic Data Engineering capabilities allow pipelines to self-heal and optimize based on historical run data.
Real-Time Intelligence
Tighter integration with Microsoft Fabric IQ allows pipelines to trigger based on complex business events, not just file arrivals.
Recommended Reading
Expand your expertise with these deep dives from the Ultimate Info Guide library:
- Fabric Lakehouse vs Data Warehouse: Which to Choose?
- Data Warehouse Optimization Techniques
- Building RAG Applications in Fabric
- Fixing OneLake Shortcut Authorization Failures
Advanced Architecture: Storage & Formats
A data pipeline is only as good as the storage layer it feeds. In 2026, understanding the underlying format nuances is critical for performance.
Delta Lake vs. Apache Iceberg in Fabric
While Fabric optimizes for Delta Lake (the native format of OneLake), many enterprises migrating from other ecosystems might be using Iceberg. Pipelines can now ingest Iceberg tables, but you must understand the trade-offs.
- Conversion: Use Copy Jobs to convert Iceberg to Delta on-the-fly for better performance with Direct Lake mode.
- Comparison: For a detailed breakdown of feature parity, read our analysis on Apache Iceberg vs Delta Lake.
Data Quality vs. Observability
We often use “monitoring” as a catch-all term, but pipeline observability goes deeper. It isn’t just about “did it fail?”; it’s about “is the data accurate?”.
- Implementation: Integrate libraries like Skrub within your Notebook activities to clean data before it hits the Gold layer.
- Strategy: Adopt a formal strategy by reading our Data Observability vs Data Quality Guide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are the top questions data engineers are asking about Fabric Pipelines in 2026.
A: When using Copilot to generate pipeline expressions, you might encounter generic errors. These are often due to context limits or temporary service interrupts. See our Copilot Fix Guide for troubleshooting steps.
A: Yes. Microsoft’s new “Operational Data Agent” allows for autonomous monitoring. Instead of writing static alert rules, the agent learns your pipeline’s baseline performance. Learn more about the Operational Data Agent and the broader Microsoft Fabric Data Agent ecosystem.
A: Fabric Pipelines are the successor to Synapse Pipelines. While 95% of activities are identical, Fabric introduces “Copy Job” and “Direct Lake” which Synapse lacks. However, there are still some migration limitations you should be aware of. Check the full Fabric vs Synapse Comparison.
A: For supported sources (like Cosmos DB, Azure SQL), Data Mirroring is superior because it offers near-real-time replication with zero code. However, for complex transformations or unsupported sources, Pipelines remain the standard.
Final Resources & Tools
To maximize your productivity, utilize these tools and guides available on UltimateInfoGuide:
AI & Automation
Leverage AI to speed up development. From Prompt Engineering for Beginners to DAX with AI, automation is key.
Security & Compliance
Ensure your pipelines are secure. Review our Cloud Security Tips and manage access correctly to avoid issues like Authorization Failures.
Power BI Integration
Pipelines ultimately feed reports. Ensure your data is ready for AI in Power BI and Next-Level Data Insights.
This guide is part of the Microsoft Fabric Tutorial Series. For non-technical tools, check out our Productivity Timer or our AI Image Enhancer.
Ready to Master Fabric Pipelines?
Start by building your first pipeline using the Execute Pipeline pattern above. Use Lookup for incremental loads, ForEach for parallelization, and Stored Procedures for audit logging. As complexity grows, leverage Copilot Expression Builder to debug expressions and implement service principal-based authentication.
If you are migrating from other platforms, consider checking our guide on Fabric vs Synapse Limitations to avoid common pitfalls.
For more technical details, consult the official Microsoft Fabric Data Pipelines Documentation and the Connector Overview.
Data Pipelines in Fabric – Complete 2026 Guide
Built with the latest Microsoft Fabric features (January 2026).
Explore more at UltimateInfoGuide.com | Fabric Production Stability Review
© 2026 UltimateInfoGuide. All rights reserved.